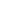-
Topics
Subnavigation
Topics
Electromagnetic fields
- What are electromagnetic fields?
- High-frequency fields
- Radiation protection in mobile communication
- Static and low-frequency fields
- Radiation protection relating to the expansion of the national grid
- Radiation protection in electromobility
- The Competence Centre for Electromagnetic Fields
Optical radiation
- What is optical radiation?
- UV radiation
- Visible light
- Infrared radiation
- Application in medicine and wellness
- Application in daily life and technology
Ionising radiation
- What is ionising radiation?
- Radioactivity in the environment
- Applications in medicine
- Applications in daily life and in technology
- Radioactive radiation sources in Germany
- Register high-level radioactive radiation sources
- Type approval procedure
- Items claiming to provide beneficial effects of radiation
- Cabin luggage security checks
- Radioactive materials in watches
- Ionisation smoke detectors (ISM)
- Radiation effects
- What are the effects of radiation?
- Effects of selected radioactive materials
- Consequences of a radiation accident
- Cancer and leukaemia
- Hereditary radiation damage
- Individual radiosensitivity
- Epidemiology of radiation-induced diseases
- Ionising radiation: positive effects?
- Radiation protection
- Nuclear accident management
- Service offers
-
The BfS
Subnavigation
The BfS
- Working at the BfS
- About us
- Science and research
- Laws and regulations
- Radiation Protection Act
- Ordinance on Protection against the Harmful Effects of Ionising Radiation
- Ordinance on Protection against the Harmful Effects of Non-ionising Radiation in Human Applications (NiSV)
- Frequently applied legal provisions
- Dose coefficients to calculate radiation exposure
- Links
Radon therapies
- Radon therapies are medicinal applications for radon.
- They include radon galleries, radon baths, radon air baths, radon steam baths and radon waters.
- The prescribing doctor must weigh up the benefits (pain alleviation) and the risk (cancer risk) for patients when prescribing radon therapies.
- Radon applications are not advised as spa treatments.

![]() View into a radon healing cave
View into a radon healing cave
In a radon treatment, radioactive radon is applied to people for medicinal purposes.
Patients are exposed to a high concentration of radon for a short period to alleviate pain for several months and so to reduce their use of painkillers for a certain period.
Radon therapies are mainly used for rheumatic diseases. These are chronic inflammatory diseases of the joints or spine, such as ankylosing spondylitis, and chronic degenerative diseases of the joints or spine, i.e. arthrosis.
Weighing up risks and benefits
Radon applications are used only when they are necessary from a medical point of view. The prescribing doctor must weigh the benefit of pain alleviation against the risk that the radon causes for the patient. The risks of the radon treatment must be compared with the risks of alternative treatment methods (for example with the possible side effects when patients take painkillers over a long period).
Radon applications are not advised as spa treatments.
Treatment methods
There are several treatment methods:
- Radon healing adits, in which patients are exposed for a few hours to an atmosphere with a high radon concentration (around ten treatments of around one hour duration per treatment) and absorb radon trough the skin and trough the lung by breathing.
- Radon baths, in which patients bathe in radon-rich water and absorb radon mainly through the skin.
- Radon air baths respectively radon steam baths, where patients sit in a covered tub in radon gas respectively radon steam and absorb radon through the skin.
- Radon waters, where patients drink spring water with high radon concentrations and absorb radon through the gastro-intestinal system.
Risks
The benefits and risks of radon therapy are controversial: Radon concentrations in radon healing caves are extremely high. Since the patients are exposed to this radon concentration only for a short time, however, their risk of developing lung cancer increases only slightly as a result of the treatment. But even this increase in risk is only justified if a corresponding medical benefit is to be expected.
If radon is absorbed mainly through the skin and/or through the gastro-intestinal system during bathing or drinking, the radiation-related risk of contracting lung cancer is significantly lower than in radon galleries because only small quantities of radon reaction products are inhaled.
Since employees at workplaces in radon spas and radon healing adits are exposed to radon more permanently than patients, their exposure to radon is regularly checked and registered in order to protect them from radon at work.
State of 2024.08.28